How to Close Port-occupied Applications
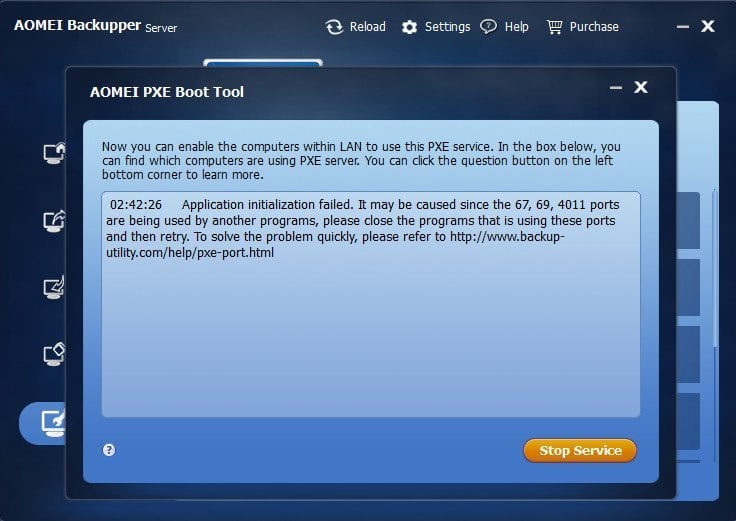
Thank you for using AOMEI PXE Boot Tool. Did you encounter problem like “Application initialization failed. It may be caused since the 67, 69, 4011 ports are being used by other programs, ……“ while using its “AOMEI PXE Boot Tool“ feature? If so, please do not worry. Now, we’re going to help you to solve this matter manually. First, please make sure that your problem is just like what the picture shows bellow.
Solution 1:
The cause of this problem can be that you already have PXE programs or program counterpart to PXE in your system. For example, you already installed other product similar to ours. Only in this situation, can the ports be occupied.
The easiest way is to temporarily uninstall the PXE and similar product you have installed, and try AOMEI PXE Boot Tool. If it’s inconvenient for you to uninstall these programs, you can also solve the above problem by ending the processes of the PXE and similar product temporarily. For details, please refer to Solution 2.
Solution 2:
1. According to the prompting, we can get to know the cause of the failure is that the three ports (67, 69 and 4011) are occupied. Therefore, to solve the problem, we only have to find out the processes or services which occupied the three ports and end them. Then, how to find out these processes or services?
2. Open “Run” with “Win” and “R” on keyboard, and key in “cmd” in “Run” to open Windows command prompt (cmd.exe).
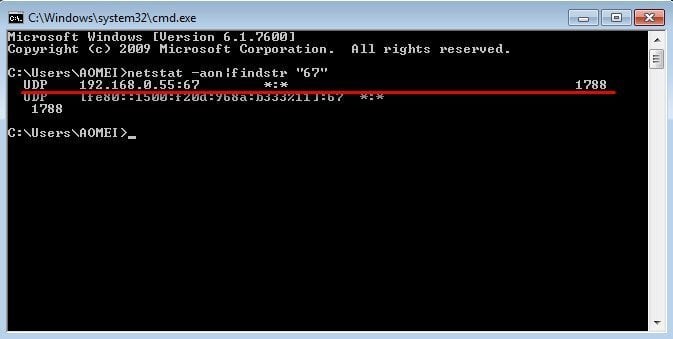
3. Then, we need to use command “netstat -aon|findstr” to check the status of ports. Most importantly, we need to find out the IDs of processes or services which occupy the three ports. For example, to check the status of Port 67, you need to input “netstat -aon|findstr ‘67’” in command prompt and click “Enter” like the following picture shows.
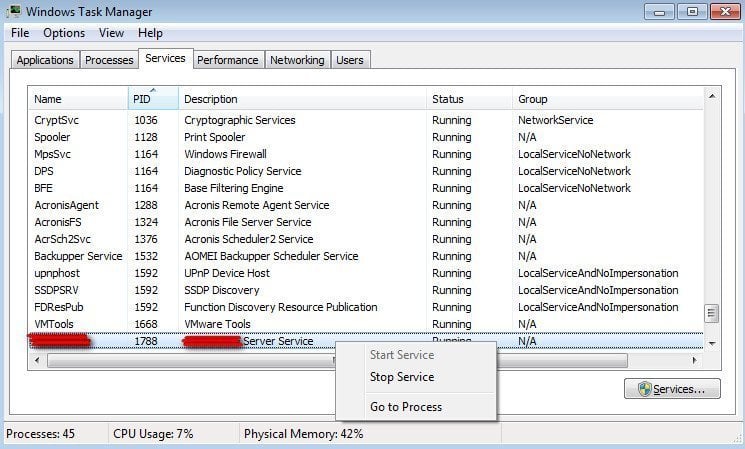
Compared with local IP address 192.168.0.55, find the process ID of Port is 1788 (the number at the end of the line). In this way, find the other two process IDs of Port 69 and 4011 and write all three process IDs down.
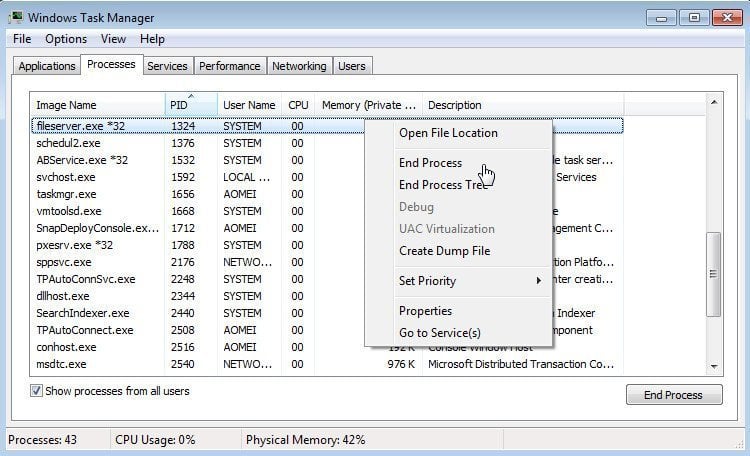
4. After all the situations of occupied ports are clear, we can find corresponding processes referring to process IDs. We will search the corresponding processes in “Processes” or “Services” in “Windows Task Manager”.
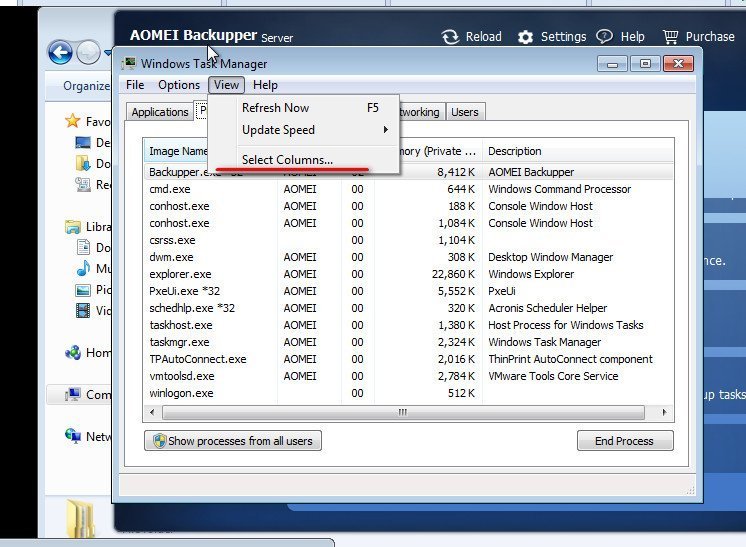
Use “Ctrl+Alt+Delete” to open “Windows Task Manager”. You might not find PID (process ID) in “Processes” or “Services”. Thus, you should first do some settings to “Windows Task Manager”. The following is the way:
a) Click “View” on the toolbar of “Windows Task Manager”.
b) Choose “Select Columns…”
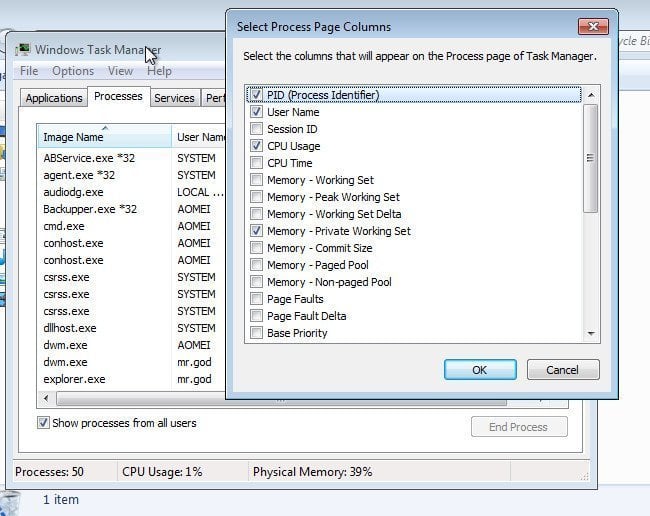
c) Tick “PID (Process Identifier)” and click “OK” to back to “Processes” or “Services”.
5. After the settings to PID, we can search the processes of Port 67, 69 and 4011 in “Processes” or “Services”. Then, end these processes manually: right-click the process and select “End Process” or “Stop Service”. Be sure to end all the processes of the three ports.
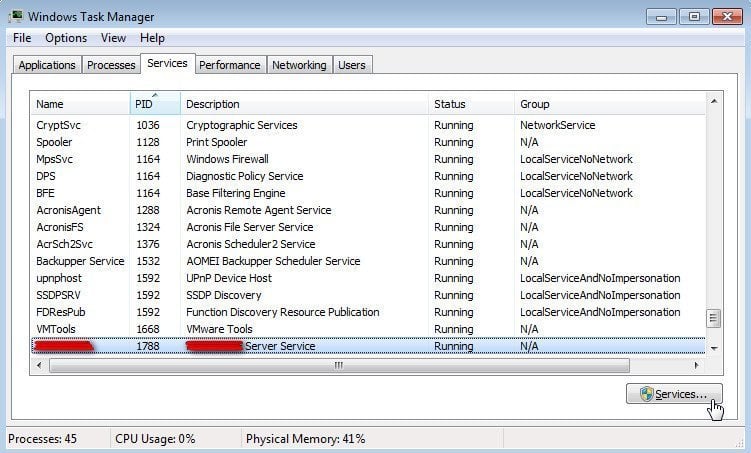
You might fail to end the processes in “Services”. Then, you can click “Services…” on the right bottom of the window to open the main interface of Windows “Services”.
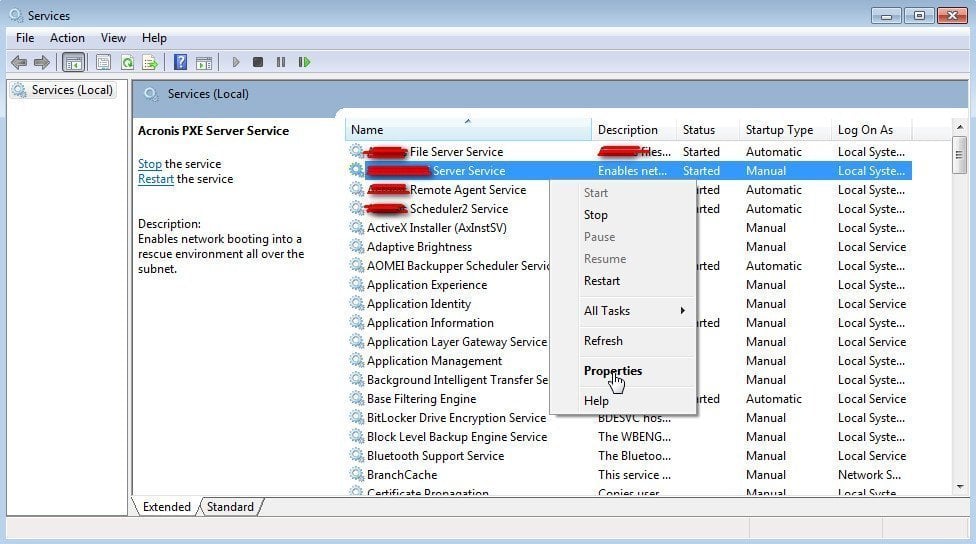
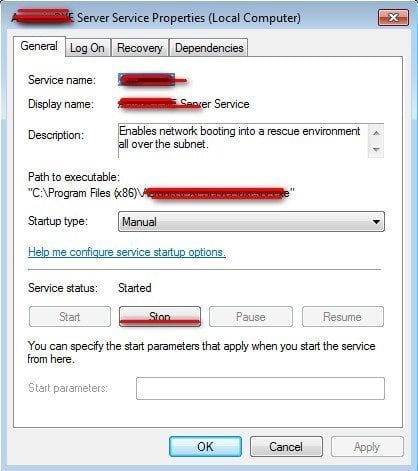
Then, find the corresponding service name; right-click it and choose “Properties”.
Click “Stop” to stop the service. Or, you can also disable “Startup type” and click “OK”.
After all the operations, you can experience “AOMEI PXE Boot” feature as following.